Arthritis is a group of conditions characterised by inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility. There are over 100 types of arthritis, but the most common forms include:
Arthritis can affect any joint in the body, and symptoms may include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Chronic arthritis can lead to joint deformity and loss of function over time.
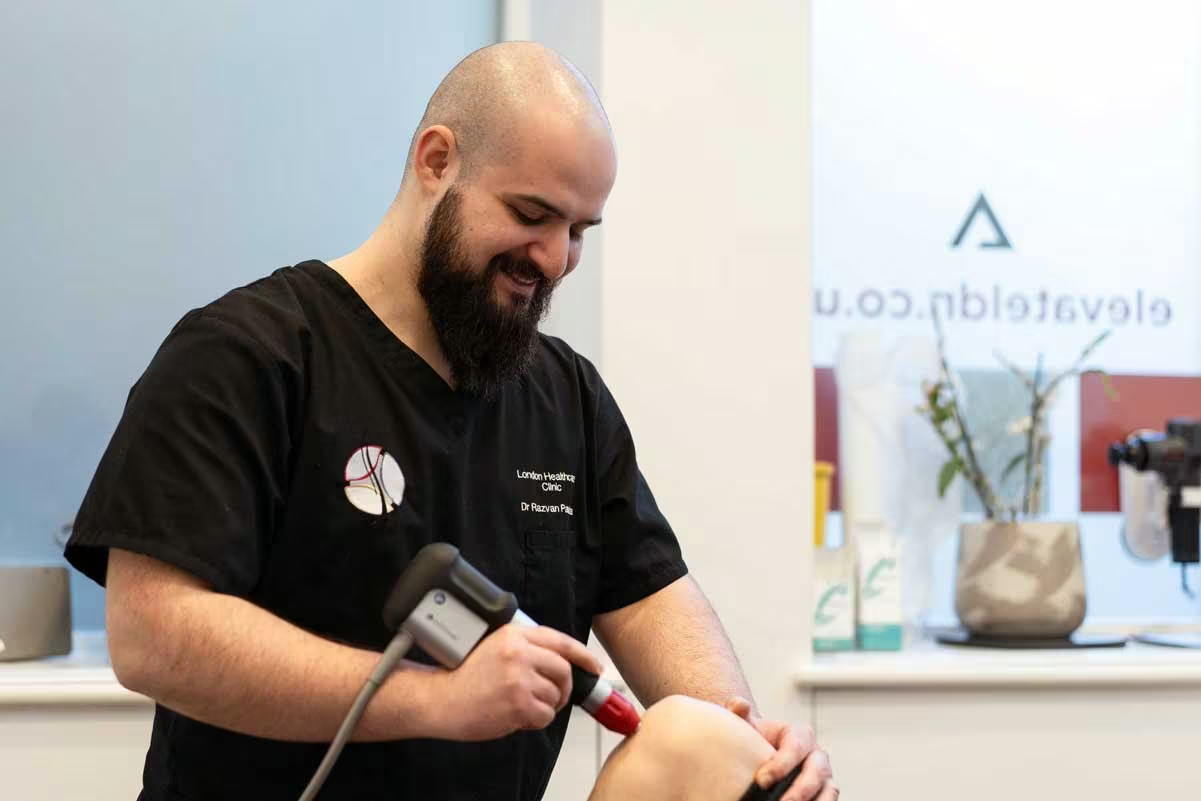
Chiropractic treatment for arthritis focuses on improving joint function, reducing pain, and enhancing mobility without invasive procedures or medications. Chiropractors use several methods:
Chiropractic care helps manage arthritis by improving joint alignment and mobility, reducing inflammation, and alleviating pain.
Physiotherapy is a key part of arthritis management, aiming to strengthen muscles around the joints, improve mobility, and reduce pain. Physiotherapists use several techniques:
Physiotherapy helps in the long-term management of arthritis by improving joint function, relieving pain, and slowing the progression of joint degeneration through regular exercise and therapy.
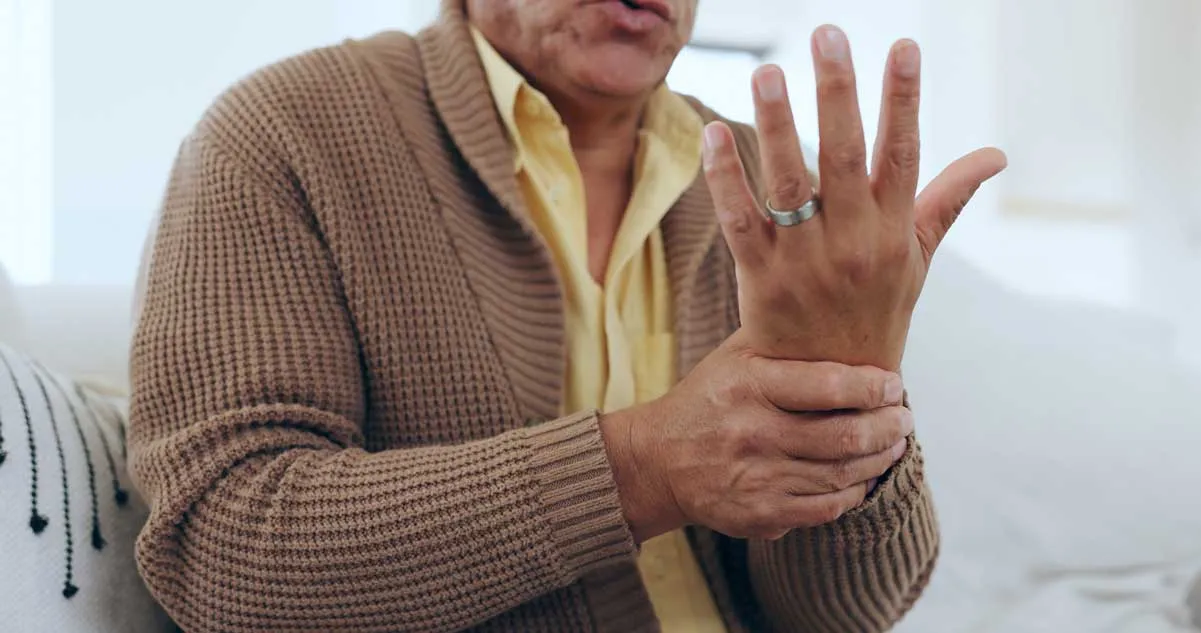

A combined approach of chiropractic care and physiotherapy can be highly effective in managing arthritis. Chiropractic care focuses on realigning joints and easing pressure, while physiotherapy strengthens the muscles, improves flexibility, and promotes long-term joint health. Together, they offer a comprehensive strategy for reducing pain, improving mobility, and enhancing the quality of life for people with arthritis.